About Us
Littering is a major problem that threatens the environment (e.g., causing fire hazards, air pollution, and street flooding), society (e.g., causing human health hazards), and the economy (e.g., causing significant expenses for administrations and municipalities). The root of littering is indeed in society and cannot be feasibly solved by the authorities alone: addressing littering requires everyones' commitment.
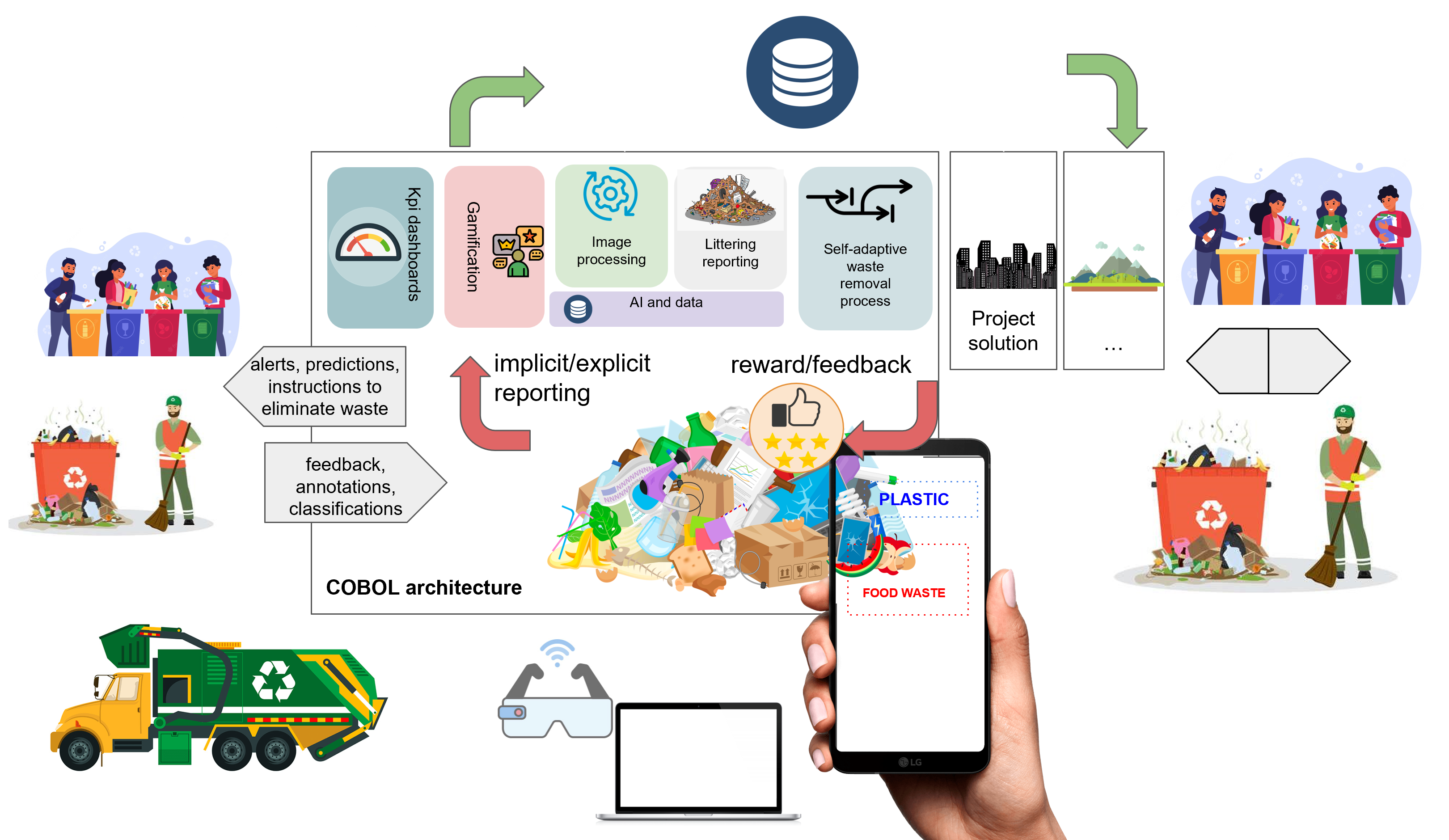
Managing littering is a multi-faceted problem that requires the cooperation of different professionals and agencies. The project focuses on illegal dumping and addresses the automated localization and identification of abandoned littering and managing its proper disposal in an integrated and flexible way. Previous approaches, including those based on citizens' engagement, were not practical enough to be successful because they required too much effort from the community or involved technical solutions that were not easily accessible by municipalities. The COBOL project will deliver key novel technical solutions that can promisingly change the level of practicality of participatory approaches for littering management. In particular, it will deliver lightweight littering reporting solutions that will enable devices to report littering transparently (e.g., automatically detecting and reporting the littering present in a selfie taken by someone) and let citizens report littering explicitly. It will deliver comprehensive engagement models involving all the stakeholders in the littering disposal process. It will collect and process data at the level of multiple communities exploiting federated learning techniques, delivering unprecedented littering prediction and detection capabilities that small rural communities can exploit that could not otherwise generate enough data to train effective models. It will deliver a model-driven self-adaptive solution that can be flexibly adapted to various contexts and deal with unexpected events to guide citizens and authorities in the waste disposal process effectively. Pilots with two municipalities will demonstrate the effectiveness of the COBOL solution.
Objectives
This project will address these challenges by developing a novel solution that can be used by administrators and policy-makers to address the littering problem
Design of a Lightweight Littering Reporting Solution
Engage Citizens in the Waste Removal Process
Establish a Comprehensive Rewarding System
Define a Littering Prediction System
Define a Highly Flexible Solution for Managing the Waste Disposal Process
Define a Decentralized Data-Processing Architecture
Develop an Open Source Implementation
Pilots with Municipalities
Deliverables
D1.1 - Software Requirements Specification 
D1.2 - A Lightweight model for waste recognition, volume estimation, and material segmentation, together with the labeled dataset collected by the community 
D2.1 - COBOL-Runtime modeling environment for the specification of BPMN models with dedicated editors and runtime interpreter
D3.1 - Set of rewarding actions that can be used and executed as part of BPMN process
D3.2 - A gamification processor that enriches the dashboard and the user profiles with gamified information
D6.1 - A decentralized, trusted framework inspired by federated and peer-to-peer systems, with proper APIs/connectors for the proficient use of the solution 
Pubblications
♢ A low-code assessment platform for urban digital twins, co-authored by Martina De Sanctis, Ludovico Iovino, Maria Teresa Rossi, Manuel Wimmer, Information and Software Technology, 2025
♢ EnseSmells: Deep ensemble and programming language models for automated code smells detection, co-authored by Anh Ho, Anh M.T. Bui, Phuong T. Nguyen, Amleto Di Salle, Bach Le, The Journal of Systems & Software, 2025
♢ Performance regression testing initiatives: A systematic mapping, co-authored by Luciana Brasil Rebelo dos Santos, Érica Ferreira de Souza, André Takeshi Endo, Catia Trubiani, Riccardo Pinciroli, Nandamudi Lankalapalli Vijaykumar, Information and Software Technology, Volume 179, 2025
♢ Architecting Federated Learning Systems: A Requirement-Driven Approach, co-authored by Luciano Baresi, Livia Lestingi, and Iyad Wehbe, accepted at the 2025 European Conference on Software Architecture (ECSA), 2025.
♢ Architecture as Code, co-authored by Alessio Bucaioni, Amleto Di Salle, Ludovico Iovino, Patrizio Pelliccione, Franco Raimondi, 22nd IEEE International Conference on Software Architecture (ICSA), 2025
♢ COBOL: COmmunity-Based Organized Littering, co-authored by Luciano Baresi, Simone Bianco, Amleto Di Salle, Ludovico Iovino, Leonardo Mariani, Daniela Micucci, Luciana Brasil Rebelo dos Santos, Maria Teresa Rossi, Raimondo Schettini, Euromicro Conference on Software Engineering and Advanced Applications (SEAA), 2024
♢ Streamlining Workflow Automation with a Model-based Assistant, co-authored by Adiel Tuyishime, Francesco Basciani, Amleto Di Salle, Javier Luis Canovas Izquierdo, Ludovico Iovino, 50th Euromicro Conference on Software Engineering and Advanced Applications (SEAA), 2024
♢ Waste Management Through Digital Twins and Business Process Modeling, co-authored by Amleto Di Salle, Arianna Fedeli, Ludovico Iovino, Leonardo Mariani, Daniela Micucci, Luciana Rebelo, Maria Teresa Rossi,, ACM/IEEE 27th International Conference on Model Driven Engineering Languages and Systems, MODELS Companion 2024
♢ On Assessing Heterogeneity Management Solutions in Federated Learning Systems, co-authored by Luciano Baresi, Tommaso Dolci, Iyad Webbe, Workshop on Distributed Machine Learning for the Intelligent Computing Continuum (DML-ICC), 2024
♢ Supporting reusable model migration with Edelta, co-authored by Lorenzo Bettini, Amleto Di Salle, Ludovico Iovino, and Alfonso Pierantonio, Journal of Systems and Software, vol 212, 2024.
♢ Efficient Litter Detection in the Wild, co-authored by Simone Bianco, Elia Gaviraghi, and Raimondo Schettini submitted to IEEE RTSI 2024 - 8th International Forum on Research and Technologies for Society and Industry.
Team

Luciano Baresi
Responsabile unitàPolitecnico di Milano

Simone Bianco
Local MemberMilano-Bicocca University

Gianlorenzo D'Angelo
Local MemberGran Sasso Science Institute

Amleto Di Salle
Local MemberGran Sasso Science Institute

Arianna Fedeli
Local MemberGran Sasso Science Institute

Ludovico Iovino
Responsabile unitàGran Sasso Science Institute

Leonardo Mariani
Principal InvestigatorMilano-Bicocca University

Daniela Micucci
Local MemberMilano-Bicocca University

Franco Raimondi
Local MemberGran Sasso Science Institute

Luciana Rebelo
Local MemberGran Sasso Science Institute

Maria Teresa Rossi
Local MemberMilano-Bicocca University

Raimondo Schettini
Local MemberMilano-Bicocca University